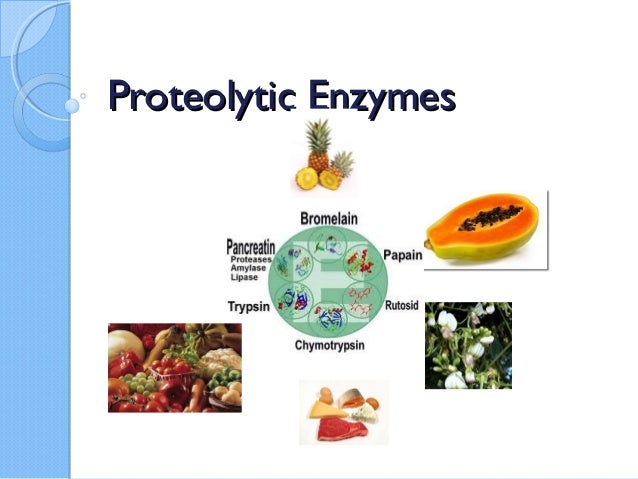
The handle the globular head and the N-terminal region. These enzymes include the pancreatic proteases chymotrypsin and trypsin bromelain pineapple enzyme papain papaya enzyme fungal proteases and Serratia peptidase the silk worm enzyme.
Serine Proteases And Regulators Creative Diagnostics
In the living organism proteolytic enzymes proteases are produced to degrade and modify proteins.

Proteolytic enzyme structure and function. Proteolytic enzymes or proteases refer to the various enzymes that digest break down into smaller units protein. A single enzyme catalyzes each reaction. StructureFunction Relationships of Proteolytic Enzymes provides information pertinent to the fundamental aspects of proteolytic enzymes.
As a result proteolytic enzyme supplements may contain both animal- and plant-derived enzymes. Enzyme ClpP is a highly conserved serine protease present throughout bacterial and also found in the mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotic cells. The chemical structure of antibodies explains three functions of antibodies.
Preparations of proteolytic enzymes. These enzymes include the pancreatic proteases chymotrypsin and trypsin bromelain pineapple enzyme papain papaya enzyme fungal. Catalysis of hydrolysis of alpha-glucosidic bonds in starch and related saccharides they are quite different.
The present review describes the structural features of alpha-amylase beta-amylase and glucoamylase that are the best known amylolytic enzymes. Pepsin chymotrypsin and trypsin are placed under the category of proteolytic enzymes. Proteolytic enzymes also known as proteases cleave the peptide bonds that connect two amino acids.
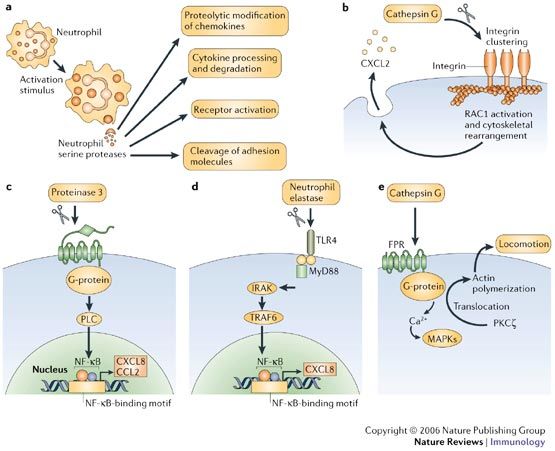
Several proteolytic enzymes either of the host and of the virus act in a concerted fashion to regulate and coordinate specific steps of the viral replication and assembly such as i the entry of the virus ii the maturation of the polyprotein and iii the assembly of the secreted virions for further diffusion. The symbols indicate the relevant structural genes encoding each of the enzymes 2 48. 1 binding versatility 2 binding specificity and 3 biological activityA mammal is capable of re-sponding to more than 100 million antigenic de-terminants and can even respond to artificial anti-gens that do not exist in nature Fast Focus 1.
Although they show similar function ie. The ClpP monomer is folded into three subdomains. This book presents the historical role of proteolytic enzyme as a group in protein and enzyme chemistry.
They are also called proteolytic enzymes or proteinases. Proteolytic enzymes or proteases refer to the various enzymes that digest break down into smaller units protein. Proteolytic enzymes are present in bacteria archaea certain types of algae some viruses and plants.
These enzymes are involved in the hydrolysis of proteins into peptides and amino acids by breaking them down into peptide bonds. Proteolytic enzyme also called protease proteinase or peptidase any of a group of enzymes that break the long chainlike molecules of proteins into shorter fragments peptides and eventually into their components amino acids. Summary Proteolytic enzymes are specific types of enzymes.
Alpha-Amylase is the alpha -- alpha retaining glycosidase it uses the retaining mechanism and beta. The history of proteolytic enzymes is intimately interwoven with that of protein chemistry. They follow a hydrolytic reaction mechanism.
Proteolytic enzymes are indicated in inflammatory conditions and to support the immune system. Proteolytic enzymes are produced by both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms in which they perform key biological functions. By itself ClpP can assemble into a tetradecamer complex 14-members.
In the very early days proteolytic enzymes were considered an impediment that had to be removed in the isolation of proteins generally. Pepsin is quite effective in breaking down peptide bonds in case of amino acids such as phenylalanine tryptophan and tyrosine. Therefore proteases involved in these three steps are important targets envisaging that.
A main task for proteolytic enzymes is to degrade proteins into peptides or amino acids to be used either as an energy source or as building blocks for resynthesis of proteins. Because the amino acid se-. The function of Proteases-enzyme Protease refers to a group of enzymes whose catalytic function is to hydrolyze peptide bonds of proteins.
They are most. Proteases differ in their ability to hydrolyze various peptide bonds.
Https Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1111 1541 4337 12326
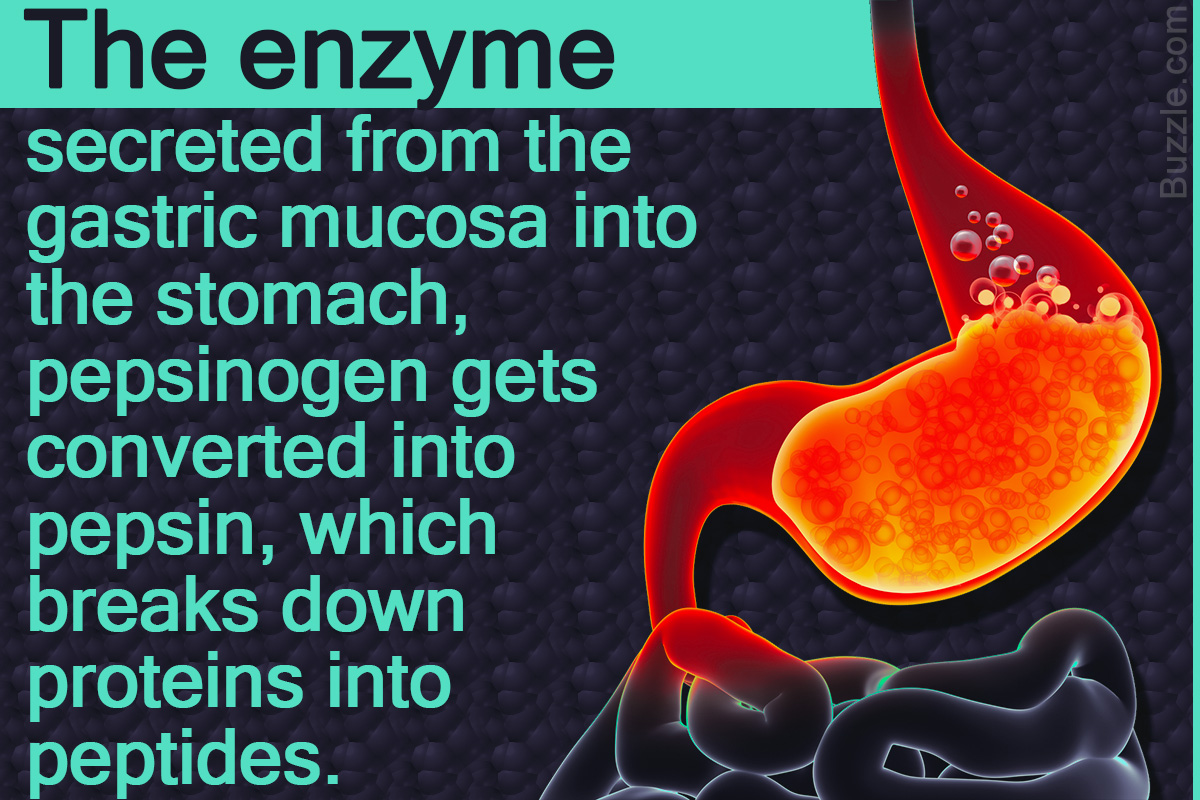
Pepsin Enzyme Structure Function And Important Facts Science Struck

Protease Enzyme Application In Food Processing

Intrinsic Evolutionary Constraints On Protease Structure Enzyme Acylation And The Identity Of The Catalytic Triad Pnas

Protease An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Hiv 1 Protease An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Https Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1111 1541 4337 12326

Proteolysis And Its Control Using Protease Inhibitors In Fish And Fish Products A Review Singh 2018 Comprehensive Reviews In Food Science And Food Safety Wiley Online Library

Intracellular Proteolytic Systems

Microbial Proteases And Application As Laundry Detergent Additive Scialert Responsive Version

Intrinsic Evolutionary Constraints On Protease Structure Enzyme Acylation And The Identity Of The Catalytic Triad Pnas

Meat Tenderization Mechanism And The Impact Of Plant Exogenous Proteases A Review Sciencedirect

Proteases History Discovery And Roles In Health And Disease Journal Of Biological Chemistry
/proteolytic-enzymes-4774179-primary-recirc-e9a3bc57768746e5ab330e5d3cb9bbfa.jpg)
Proteolytic Enzymes Benefits Side Effects Dosage And Interactions

Protease An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
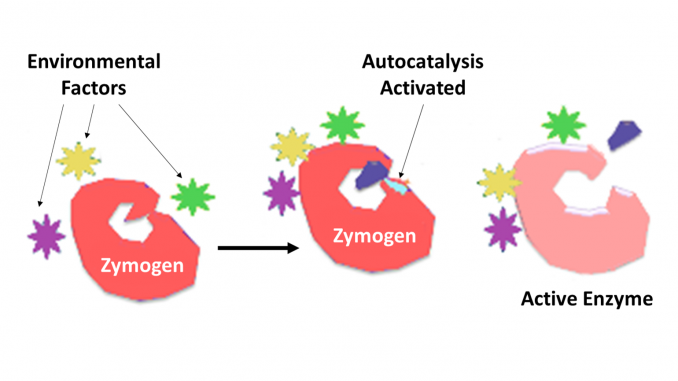
Zymogen Introduction Creative Enzymes Blog
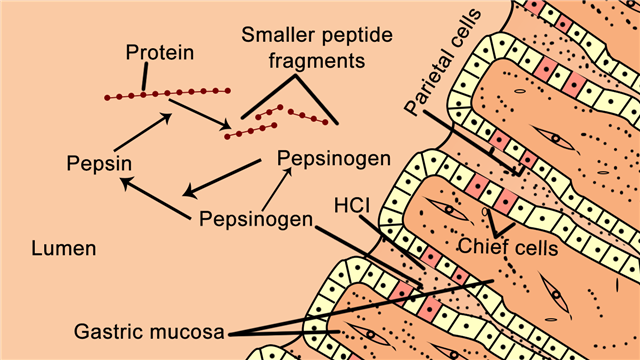
Pepsin Enzyme Structure Function And Important Facts Science Struck